Description
Name: choline
CAS£º 62-49-7
Definition£º
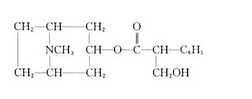
Choline is a quaternary saturated amine with the chemical formula (CH3)3N+CH2CH2OHX−, where X− is a counterion such as chloride (see choline chloride), hydroxide or tartrate. Choline chloride, in mixture with urea is used as a solvent (DES) and the salicylate salt is used topically for pain relief of aphthous ulcers.
Choline and its metabolites are needed for three main physiological purposes: structural integrity and signaling roles for cell membranes, cholinergic neurotransmission (acetylcholine synthesis), and as a major source for methyl groups via its metabolite, trimethylglycine (betaine) that participates in the S-adenosylmethionine synthesis pathways.
Apply:
1¡¢Contribute to treatment of Alzheimer's disease
2¡¢Treatment of nervous system diseases such as Parkinson's disease and tardive dyskinesia helpful
3¡¢Control fat and cholesterol savings
4¡¢Promote liver function, help the body eliminate toxins organization
5¡¢Help send a signal to stimulate the nerve, prevent old age memory loss.
Deficiency:
Lack of long-term intake of dietary choline may include the main findings of the liver, kidney, pancreas disease, memory disorders and growth failure.
1¡¢the liver changes: most of the animals, the lack of choline can cause liver dysfunction, a large number of liver lipid (mainly triglyceride) accumulation and eventually filled the entire liver cells.
2¡¢kidney changes: lack also harmful to the kidneys shrink cholinergic function.
3¡¢induced cancer: lack of choline caused by genetic damage caused by carcinogenic process first, and then some can form tumor cell survival and proliferation of variations.
4¡¢Low-choline diet-related symptoms£ºinfertility, growth retardation, bone abnormalities, blood disorder and hypertension were also reported.
More